Good sources which provide adequate explanation about corporate banks are very limited, whilst sources that discuss investment banks are readily available everywhere. As someone who successfully made a jump into corporate banking, I dedicate this post to those who are interested in starting a career in a corporate bank or those who wants to know more about corporate banking industry.
Corporate Bank vs Investment Bank
Corporate bank and investment bank have different business models. Think of corporate banking and investment banking as type of services whereas a single bank can offer both investment banking and corporate banking services in parallel.
- Corporate bank takes deposit and extends loans to corporate clients. On top of this, corporate bank also provides wider array of services such as cash management services, trade finance, custody services, hedging, and other structured loan products. Profit is mainly generated from the spreads between deposit and lending rates.
- Investment bank meanwhile acts as the intermediary for corporate clients who wish to raise fund in the capital market, either through debt or equity issuance. Investment bank may also acts as advisors for corporate clients in merger and acquisition and corporate restructuring. Profit is generated from commission fee for successful deals.
Corporate Bank’s Structure
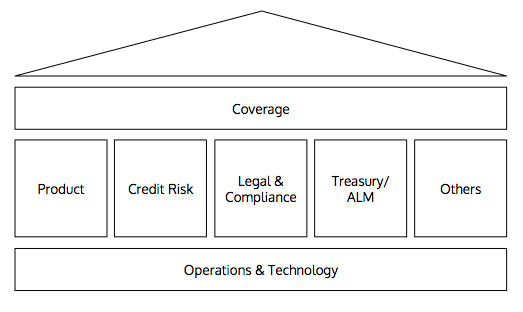
As depicted above, coverage acts as the face of the bank, connecting clients with the bank. Coverage is also supported by various middle roles such as product, credit risk, legal & compliance, and Treasury. There are also other support functions such as strategy, special account management, human resources, corporate affairs, and brand & marketing that make the bank whole. Finally, operations & technology serve as the backbone, crucial in executing bank’s businesses.
Coverage
Coverage originates and maintains existing client portfolio. Coverage actively identifies new business opportunities, as well as monitors the credit exposure. In layman’s term, coverage is the salesperson. Coverage can further be broken down based on industry types and sizes, commonly as follows:
- Financial institution (banks and non-banks)
- Global subsidiaries/ multi-national companies
- Large local corporate
- State-owned enterprises (“SOE”)
- Small medium enterprises (“SME”)
There are various roles within coverage, which are:
- Relationship manager (“RM”) is the main point of contact for each corporate clients. RM shall have deep understanding of client profile and needs. RM shall have at least general understanding of products the bank offers.
- Assistant relationship manager (“ARM”) assists RM in performing its role.
- Credit analyst determines the creditworthiness of prospects and existing clients, by analysing client’s quantitative and qualitative performance. Credit analyst shall have expertise in financial accounting and risk analysis.
Product
Corporate bank provides various products, which can be classified as follows:
- Transaction banking
- Trade finance, e.g. letter of credit, bonds and guarantees, invoice-based loan, and supply chain financing.
- Cash management, e.g. virtual accounts, current account saving account (“CASA”), time deposit (“TD”), sweeping, pooling, payment services.
- Custody
- Financial markets, e.g. spot, forward, cross-currency swap
- Loan syndication
- Others, e.g. project finance, aircraft financing, vessel financing
Couple roles within products are:
- Product partner assists RM by providing their expertise in a specific product. Product partner also structures the products in such a way that both client needs and bank’s appetite are fulfilled
- Product manager continuously looks for improvement in product by observing market trends. Product manager ensures new products are rolled out successfully and comply with regulations.
Treasury
Treasury/ ALM (“asset liability management”) is the bank’s bank, managing the bank’s liquidity. Treasury calculates the bank’s cost of funding daily, called FTP (“funds transfer pricing”), which is then used as a base to determine interest rate for client’s credit facility, CASA, and TD. To ensure profitability, lending pricing shall be above FTP, whilst funding pricing shall be below FTP.
Credit Risk
Credit risk manages the bank’s credit risk portfolio. Credit risk reviews and decides whether new credit line proposed by coverage will be approved. Credit risk is the final gate to ensure rate of non-performing loan is low. Seniors in credit risk have higher thresholds for approving credits.
Legal & Compliance
Legal provides legal advices in evaluating risks associated with completing deals and transactions. Meanwhile, compliance ensure the bank complies with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations. Both legal and compliance regularly socialises regulation changes to the bank’s employees to prevent regulation breach and/or non-compliant actions. Legal & compliance’s roles have recently become increasingly vital as banks would like to not only avoid incurring penalty, but also uphold their existing brands and reputations.
Operations & Technology
Operations & technology serve as the backbone of the bank, typically consists of a very large number of people. As operations & technology is crucial to deliver the bank’s business, operations capability needs to be regularly enhanced by increasing efficiency to handle high volume processing.
Summary
Depends on your expertise and aspirations, corporate banks offer a wide array of roles across functions. If you have no idea what you are getting into, I would recommend you entering via graduate program and targeting roles within coverage. Coverage is widely considered as revenue generator and one of the sexy roles within corporate banking. This means, your high performance will be highly rewarded with appreciation and huge chunk of annual bonus.
Operations & technology, on the other hand, are generally considered unsexy. Many roles within operations & technology are mundane and clerical, with less appreciation and meh bonus. I do not want to belittle their roles within the bank, however, reality in the industry said so. If you have to get into operations & technology and you are an ambitious person, pick project management roles that are much more fulfilling than mundane administration tasks.
Other than coverage, financial markets and treasury roles are also considered highly sexy and may award you with large bonus.